What Is Behavioral Medicine: An Overview
Updated: June 19, 2024

Do you have an interest in medicine, health, science, behavior, and psychology? The interdisciplinary field of behavioral medicine (BM) combines various biomedical concepts to help diagnose and treat patients. Behavioral medicine goes deeper than the surface level of issues and helps patients adjust their own behavior so that they can be a part of their own treatment methods. The science behind it all is based on the connection between the mind and body.
As a newly developing field, behavioral medicine offers an intriguing career path for many. Let’s take a look at how this field is evolving, what kind of ailments it helps to treat, and other related degrees like health science.
- Photo by Mark Williams on Unsplash
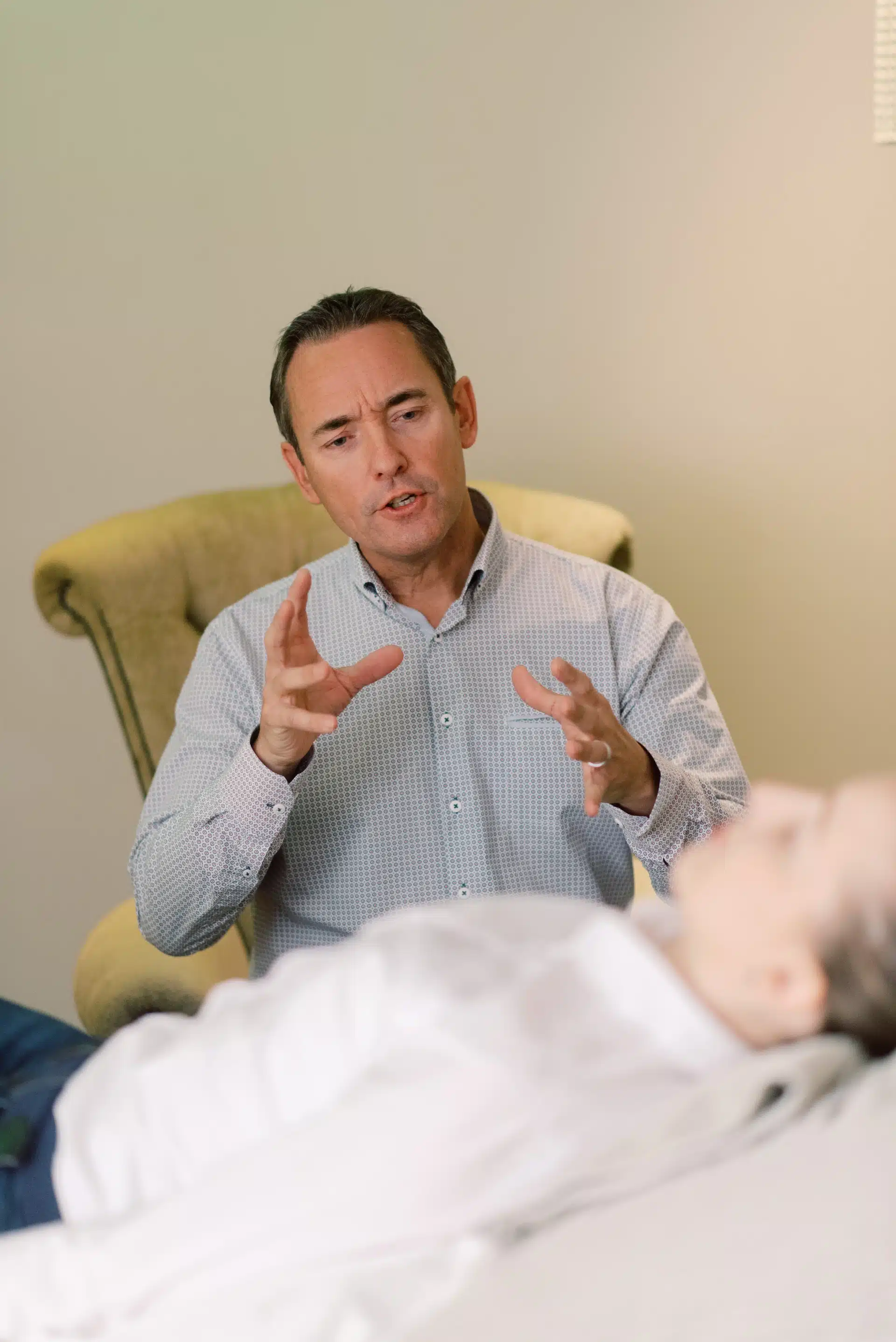
What is Behavioral Medicine?
Behavioral medicine combines biomedicine, behavioral, and psychosocial concepts to work with patients who are experiencing psychosomatic disorders. In simplistic terms, it can be considered “mind-body medicine” as it looks to both physical and mental circumstances to help diagnose and treat ailments.
Patients of all ages can take part and reap the benefits of behavioral medicine. The field leverages behavioral health techniques to approach a variety of mental health and medical conditions.
In the same vein, professionals from various health-related backgrounds can become trained in these methods and techniques.
A Little Bit of Background
Born from psychosomatic medicine, behavioral medicine got its start during the 19th century. This is when psychoanalysis therapists started recognizing that many medical disorders are caused or exacerbated by behavioral patterns and habits.
At Stanford in 1975, the first research laboratory was created for the purpose of behavioral medicine. In the 1980s, further investment in this field took place, and today, the science and field continues to grow in research and practice.
How Behavioral Treatment Works
Behavioral medicine specialists rely on different types of psychological interventions to help relieve, prevent, or ease physical, emotional, or mental issues on behalf of their patients. Rather than targeting the symptoms directly, BM specialists seek to get to the source of the problem.
To illustrate, if a patient is suffering from a migraine that gets worse with emotional turmoil, a BM specialist will try treatments like diaphragmatic breathing, mindfulness, or other stress-relief techniques. In this way, a patient’s own behaviors can work to reduce their symptoms.
Just like any type of medicine, the treatment or plan of action will depend on the patient’s needs. But, with BM, you will utilize techniques like:
Desensitization
Patients list what makes them sensitive and then the therapist teaches relaxation techniques during these situations to reduce sensitivity
Extinction
By repeatedly exposing patients to high-anxiety situations, anxiety may ultimately be reduced once the patient realizes the outcomes aren’t so bad.
Reinforcement
Patients are positively rewarded (reinforce) as a result of performing the desired behavior.
Flooding
To rid a patient of phobias or fears, they may be exposed to what they so fear for a long period of time so that they can get over the fear.
Mindfulness Therapy
A focus on meditation which can be used to reduce chronic episodes or boost one’s awareness so that they can have better control of their emotions.
Distress Tolerance
Helps patients deal with pain by using distraction techniques.
Required Education
While there isn’t a specific standard certification process in this field, a professional in the healthcare sector can call themself a behavioral medicine specialist if they satisfy certain conditions.
Behavioral medicine specialists can have a variety of different degrees, including a: BS, BA, MD, EdD, PsyD, PhD, DDS, MBA, etc. Pursuing a specialized certificate program in behavioral health can also be the right first step in the field.
They may work as a physician, health educator, psychologist, researcher, nurse, pharmacist, geneticist, social worker, or more.
To become a BM specialist, they should complete at least two years of specialized training in the BM techniques, like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), relaxation training, biofeedback, etc.
Areas of Research and Treatment
Biomedical specialists can treat a long list of issues. This is because many diseases and ailments stem from certain behaviors or mind-body connections. These could include:
- Chronic pain (TMJ, fibromyalgia, IBS, etc.)
- Insomnia
- Obesity
- Asthma
- Skin disorders
- Sexual disorders
- Cardiovascular diseases (hypertension, coronary heart disease, etc.)
- Photo by Omid Armin on Unsplash
Who Can B-Med Help?
Behavioral medicine may seem a little off the beaten path of standard protocols, but it has been proven to help resolve many different issues. Some patients who can benefit from behavioral medicine and its practices are those who:
- Suffer from a condition that gets worse with stress or other psychological factors
- Are diagnosed with depression or anxiety and want to reduce symptoms
- Are looking to make major behavioral changes and be active in their own treatment
Related Degrees
If an interdisciplinary approach to medicine and health is what you’re looking for, then a degree in health science can be a great fit. Health science applies science to both human and animal health.
With a degree in this field, you can choose to further specialize and learn about behavioral medicine. But, even if you take another path, this degree can open the door to becoming a therapist, working in medical support roles, being a technician in the healthcare sector, or even working to help diagnose patients.
At the University of the People, our health science program is designed to prepare graduates to enter the medical, health, and wellness sectors. Like all of our degree offerings, it is tuition-free, accredited, and entirely online. You can earn your degree at your own pace. Since everything takes place online, there are no geographic or physical barriers. This allows students from all around the globe to connect and learn together from the comfort of their own homes.
Final Thoughts
There are many paths to becoming a behavioral medicine specialist. Because the field is relatively new, there isn’t a specific and globally recognized certification process. Instead, professionals can get trained in behavioral medicine techniques with multiple different educational backgrounds.
From social workers to nurses, doctors and dentists, professionals from all walks of life are learning about behavioral medicine. As people continue to recognize the immense connection between the mind and body, it’s been proven that these types of stress-relieving practices can promote better health and wellness overall.